A characteristic is a description of a thing. For example a characteristic could be the color of a shirt.
- A characteristic provides an extensible list of descriptive terms for a category or thing.
Creating characteristics
Characteristics can have the following default variable types. For more complex characteristics, a state machine will be required.
See also: data file formats.
A characteristics file can point to other category files, using the "INCLUDE" tag, to make the files more manageable. This also allows the inclusion of characteristics files created by other authors.
Characteristics are defined using the following syntax:
Characteristic Title
The characteristics title describes the fact that the definition is for a characteristic and the name of the characteristic.
Characteristic: [category name]
Characteristic Attributes
The attributes of a characteristic describe the variable type to be used and if the variable type is a state machine, the name of the state machine.
type is [variable type or "state-machine"]The type can be any of the variable types defined below, or for more complex requirements can be defined by a state machine.
state-machine is [state machine name]This specifies the state machine to be used to model this characteristic.
default value is [value]The default value represents the value the thing will have then it is created using a characteristic as a template or when loaded from a data file defining a specific thing.
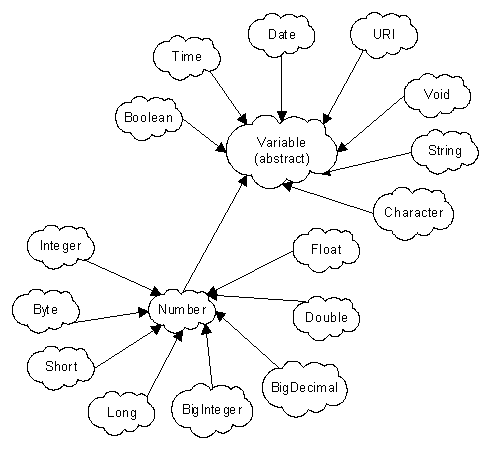
variable types
These variable types represent the internal variable storage of the system and as such are globally applied to all data. Any conversions from these types to a local flavour is done in the input and output processing systems. For example: ????
The process of the data files from the HTML format will process the input according to the selected locale string into the internal format. If no locale string is specified, the internal format is used.
The variable types come in a hierarchy. This hierarchy is based on the Java classes to allow for easy mapping with consideration for the Object Oriented XML schema as listed on the w3c site.
The reason for the proliferation of numeric types is a bit historic. By using the smallest type possible, generally the programs will operate more quickly.
!State machines are missing from this model. They are another type of variable!
!Remove the URI object!
A state machine is a special type of variable. For the programmers amongst you, enumerated types are represented by state machines. See the state machines page for more details.
definitions
Big-Decimal An arbitrary large decimal number. Big-Integer An arbitrary large integer number. Bit-Set This represents a arbitrary number of bits. Boolean A "True" or "False" value. Byte An 8 bit number from --128 to 127 inclusive. Character An single unicode character, including any ideogram from an ideographic language system. Color A RGB representation of color. All colors are unsigned byte values.
red green blue White 255 255 255 Light grey 192 192 192 Gray 128 128 128 Dark Gray 64 64 64 Black 0 0 0 Red 255 0 0 Pink 255 175 175 Orange 255 200 0 Yellow 255 255 0 Green 0 255 0 Magenta 255 0 255 Cyan 0 255 255 Blue 0 0 255 Date A date represents a number of milliseconds after an epoch. The epoch is the earliest date available in a game. Dimension2D A 2 dimensional width and height. Double An IEEE 754 number between -1.175,494,35 10E308 and 1.175,494,35 10E308 inclusive. Float An IEEE 754 number between -3.40282347 10E38 and 3.40282347 10E38 inclusive. Integer A 32 bit number between -2,147,483,648 and 2,147,483,647 inclusive. Long A 64 bit number between -9,223,382,036,854,775,808 and 9,223,382,036,854,775,807 inclusive. Number Any number in any format. The system will end up using Big-Decimal internally. Point2D A 2 dimensional point (x,y). Polygon2D A series of points that represent a 2d polygon. Rectangle2D A Point2D and a Dimension2D to fully specify a rectangle. Short A 16 bit number between -32,768 and 32,767 inclusive. String Any sequence of unicode characters not beginning with a space character. Void A thing that has no value.
Note that the state machine name can be used as a variable type.
Default world characteristics
This section describes the characteristic provided in the default world.
Object Model
Characteristics can actually be any type of object. In addition to the standard Java classes, a special set of state machines are provided to model real world characteristics.
- Characteristics are used to allow the author to be able to customise any thing.
- Characteristics used in categories are inherited by sub-types of category.
- Characteristics used in categories must be supplies with a default value.
- Characteristic values can be altered by game authors.
- Characteristic values can be changed as the game is played.
- Characteristic values are stored as part of the persistence processing.
The table below shows some typical uses for various classes in Java for characteristics. You should generally limit the use of classes to this set of classes.
A special set of objects are supplied to model characteristics. These are state machines.
| Object | Sample Use | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Big-Decimal | ||
| Big-Integer | ||
| Bit-Set | ||
| Boolean | ||
| Color | Color of a fountain pen | A fountain pen can be filled with different colors of ink. This attribute shows the current color. |
| Date | date of birth | Date the thing came into existence. |
| Dimensions | ||
| Double | ||
| Float | ||
| General-State-Machine | states for a lockable door. | Record the door as a single object with a complex 4 state model, for open and locked, open and unlocked, closed and locked and closed and unlocked. |
| Graphics | ||
| Gregorian-Calendar | ||
| Integer | ||
| Image | a picture of the object. | Supplies a picture to be shown in the HTML view of the object. |
| Linear-State-Machine | health of the player's character. | Allows setting of maximum, minimum health levels and for integer steps in the health. |
| Long | ||
| Point | ||
| Polygon | ||
| Rectangle | ||
| Simple-Time-Zone | ||
| String-Buffer | name of a character. | Allows the name of a character to be set and changed. |
| String | ||
| URL |
! Include objects from the new Java 2d and 3d models or for audio...
Representations
A representation is a special type of characteristic that cannot be modelled within the general model as characteristic. The representation provides a game level view of the object using any arbitrary modelling scheme. Examples of representations are:
- a icon,
- a picture,
- a sound,
- an avatar, or
- a 2D or 3D model.
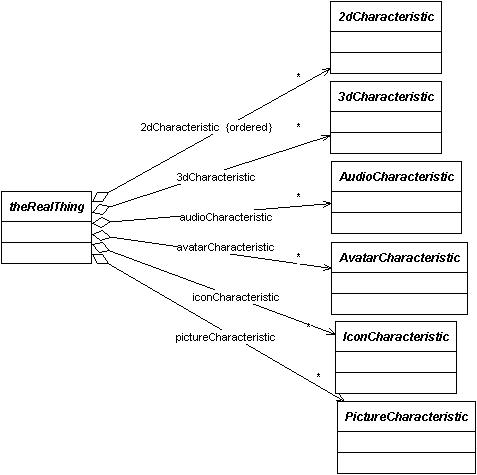
All of the pointer sets from Thing to characteristic are hash tables. This allows mapping and matching the particular representation as required within the view generators. For example: a door would be supplied with an open icon and a closed icon. So long as the labels for these icons match the table for the state, then the correct icon will be displayed.
Using characteristics
This section describes how to use characteristics when creating more complex objects such as categories and things.
22/11/99